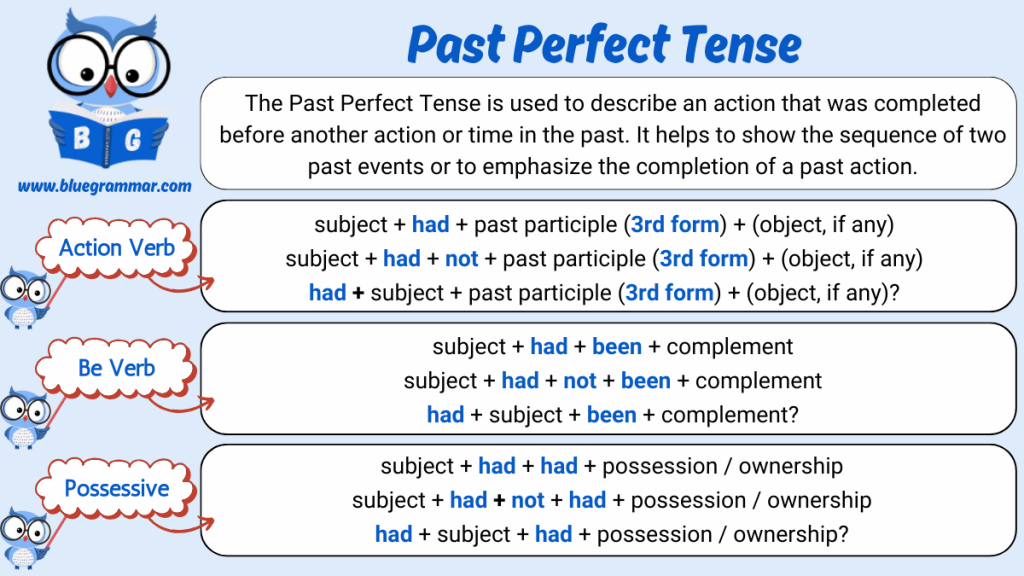
The Past Perfect Tense is used to describe an action that was completed before another action or time in the past. It gives a clear timeline and helps us understand which past action happened first. This tense is commonly used in storytelling, reports, and when reflecting on past experiences or sequences.
This tense emphasizes that one past action preceded another past event. We use it in following cases:
- To describe an action completed before another action or time in the past
- To explain causes or reasons for a past result
- To describe life experiences before a point in the past
- To show chronological order clearly
Past Perfect Tense : Action Verb
Why We Use Action Verbs in Past Perfect?
Action verbs describe physical or mental activities like “write,” “run,” “think,” or “eat.” In the Past Perfect Tense, these action verbs help us explain what had already happened before something else took place in the past.

Structure for Positive Sentences
Subject + had + past participle (V3) + object (if any)
“Had” is used with all subjects (I, you, he, she, it, we, they)
Examples With Object:
- He had written a novel before he turned 30.
- I had eaten my lunch when she arrived.
- They had completed the project before the deadline.
- She had opened the gift before I came.
- We had booked the tickets before the prices increased.
Examples Without Object:
- She had left early.
- I had slept well.
- They had arrived late.
- You had studied hard.
- He had cried after the movie.
Structure for Negative Sentences
Subject + had not + past participle (V3) + object (if any)
Examples With Object:
- I had not finished my work when the bell rang.
- They had not played football before that day.
- She had not received the message.
- He had not cleaned his room.
- We had not visited the museum before.
Examples Without Object
- I had not slept.
- She had not arrived yet.
- They had not spoken.
- You had not cried.
- He had not responded.
Structure for Interrogative Sentences
Had + subject + past participle (V3) + object (if any)?
Examples With Object:
- Had he written the report?
- Had they watched the movie before?
- Had you completed your assignment?
- Had she sent the email?
- Had we called the doctor?
Examples Without Object:
- Had I slept?
- Had she left?
- Had they arrived?
- Had you cried?
- Had he responded?
Past Perfect Tense : Be Verb
Why We Use Be Verbs in Past Perfect Tense?
“Be” verbs in the Past Perfect Tense describe someone’s identity, role, or condition that had existed before another point in the past. Unlike action verbs, “be” verbs focus on states of being, such as being a teacher, being happy, or being late.
Use “had been” for all subjects.
We use “had been” to:
- Describe a state or identity in the past that changed later
- Explain previous roles or condition
- Show temporary states of behavior or mood

Structure for Positive Sentences
Subject + had been + adjective/noun/phrase
Examples:
- He had been a teacher before he became a writer.
- They had been friends for many years.
- She had been ill before the holidays.
- I had been very tired after the journey.
- We had been excited before the match began.
Structure for Negative Sentences
Subject + had not been + adjective/noun/phrase
Examples:
- He had not been serious about his studies.
- They had not been ready for the trip.
- She had not been confident during the interview.
- I had not been honest with my parents.
- You had not been helpful at that time.
Structure for Interrogative Sentences
Had + subject + been + adjective/noun/phrase?
Examples:
- Had he been a good player?
- Had they been tired?
- Had she been sad?
- Had you been helpful?
- Had I been a good friend?
Past Perfect Tense : Possessive Verb
Why We Use Possessive Verbs in Past Perfect Tense?
Possessive verbs like have and has change to had in the past perfect tense. They show ownership, relationship, or experience that existed before a certain moment in the past.
We also use “had had” (yes, double “had”) when the main verb is “have.” Though it may sound odd, it is grammatically correct.

Structure for Positive Sentences
Subject + had + had + object/experience
Examples (Correct Usage) With Object:
- I had had a car before I moved abroad.
- She had had a good job in the city.
- We had had many pets when we lived in the village.
- He had had a lot of friends in college.
- They had had some problems before the manager arrived.
Examples With Experience:
- I had had a wonderful vacation.
- She had had a great time at the party.
- They had had trouble finding the location.
- He had had an interesting discussion with the team.
Structure for Negative Sentences
Subject + had not + had + object/experience
Examples:
- I had not had any experience with coding.
- She had not had her breakfast.
- They had not had a chance to speak.
- He had not had any savings.
- We had not had internet access.
Structure for Interrogative Sentences
Had + subject + had + object/experience?
Examples:
- Had he had any training before the job?
- Had they had dinner?
- Had you had that experience before?
- Had she had any difficulties?
- Had I had enough practice?
Important Notes:
Use Past Perfect to show an action was completed before another past event:
- Example: I had eaten before they arrived.
Do not use “had” for simple past events that don’t involve a sequence:
- Incorrect: He had went to school yesterday.
- Correct: He went to school yesterday.
“Had been” is used with both state verbs (be, feel) and roles:
- He had been angry.
- She had been a manager.
Use “had had” carefully; it’s grammatically correct though it sounds repetitive:
- I had had enough rest before the trip.