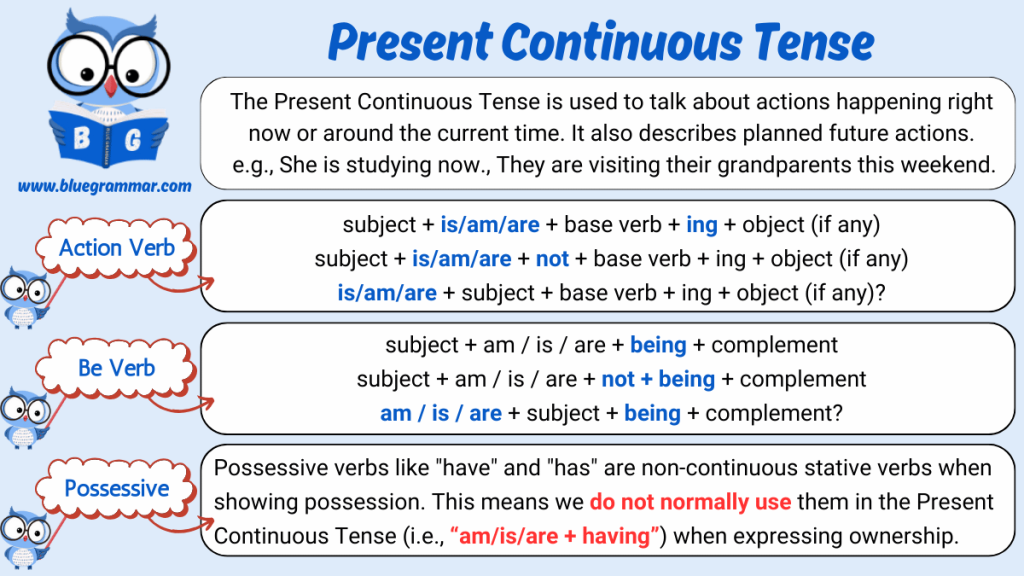
Present Continuous Tense : Action Verb
The Present Continuous Tense is used with action verbs to describe actions that are happening right now, around the current moment, or temporary actions. The main verb is used in its -ing form.

Making Positive Sentences
Structure:
Subject + am/is/are + verb(-ing) + object (if any)
Use am with “I”
Use is with he, she, it
Use are with you, we, they
Examples with Object:
He is reading a book.
They are playing cricket.
Examples without Object:
She is running.
I am sleeping.
Making Negative Sentences
Structure:
Subject + am/is/are + not + verb(-ing) + object (if any)
Examples with Object:
He is not eating meat.
We are not watching TV.
Examples without Object:
I am not singing.
She is not walking.
Making Interrogative Sentences
Structure:
Am/Is/Are + subject + verb(-ing) + object (if any)?
Examples with Object:
Is he reading a newspaper?
Are they doing homework?
Examples without Object:
Am I working now?
Is she smiling?
Present Continuous Tense : Be Verb
“Be” verbs themselves are not used in the continuous form for state expressions (e.g., am being, is being) unless referring to temporary behavior or unusual actions.
Correct (temporary behavior):He is being rude today.
Incorrect (permanent state): He is being a teacher. Instead: He is a teacher.
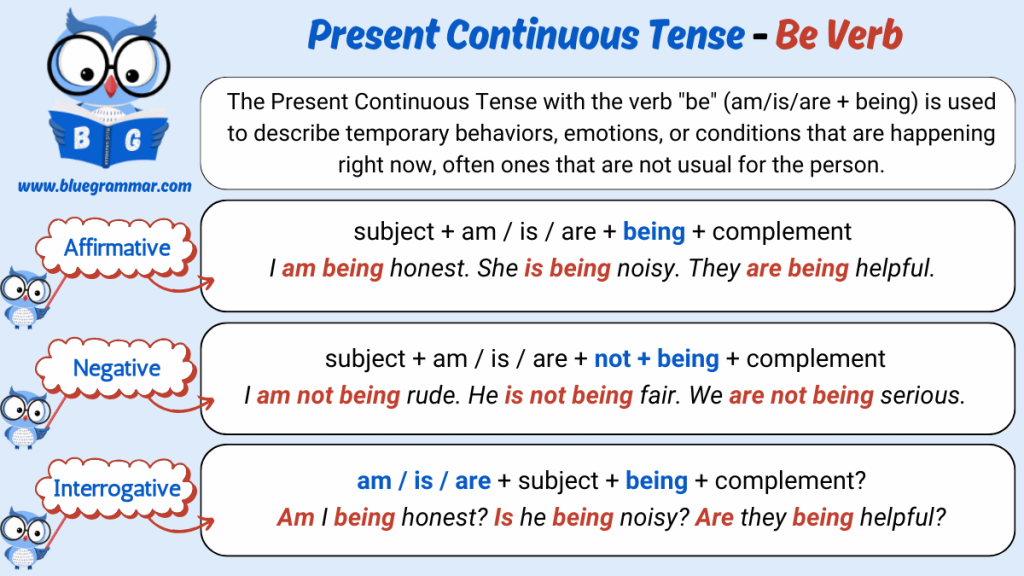
Making Positive Sentence
Structure:
Subject + is/are/am being + adjective/phrase
Examples:
You are being kind.
I am being honest.
Making Negative Sentence
Structure:
Subject + is/are/am not being + adjective/phrase
Examples:
He is not being serious.
They are not being fair.
Making Interrogative Sentence
Structure:
Is/Am/Are + subject + being + adjective/phrase?
Examples:
Is he being rude?
Are they being helpful?
Present Continuous Tense : Possessive Verb
Possessive verbs like have and has are not typically used in the Present Continuous Tense to show ownership or permanent possession.
However, “have” can be used in the continuous form when it refers to temporary experiences or actions (e.g., having dinner, having fun, having a meeting).
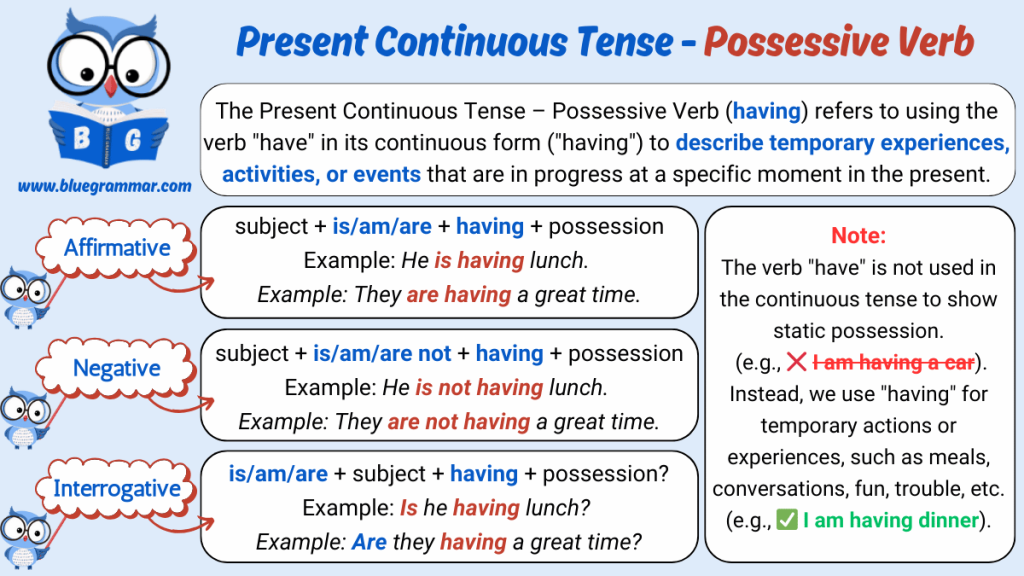
Making Positive Sentences
Structure:
Subject + am/is/are + having + object/experience
Examples with Object:
She is having lunch with her friends.
I am having a coffee break.
Examples without Object (implied action or experience):
We are having fun.
He is having a hard time.
Making Negative Sentences
Structure:
Subject + am/is/are + not + having + object/experience
Examples with Object:
He is not having his usual breakfast today.
They are not having a party this week.
Examples without Object:
I am not having fun today.
She is not having an easy time at work.
Making Interrogative Sentences
Structure:
Am/Is/Are + subject + having + object/experience?
Examples with Object:
Are you having a meeting?
Is he having dinner now?
Examples without Object:
Am I having a good time?
Are they having trouble?
Important Note:
Use Present Simple (have/has) instead of Present Continuous when talking about permanent possession:
Correct: I have a car.
Incorrect: I am having a car.