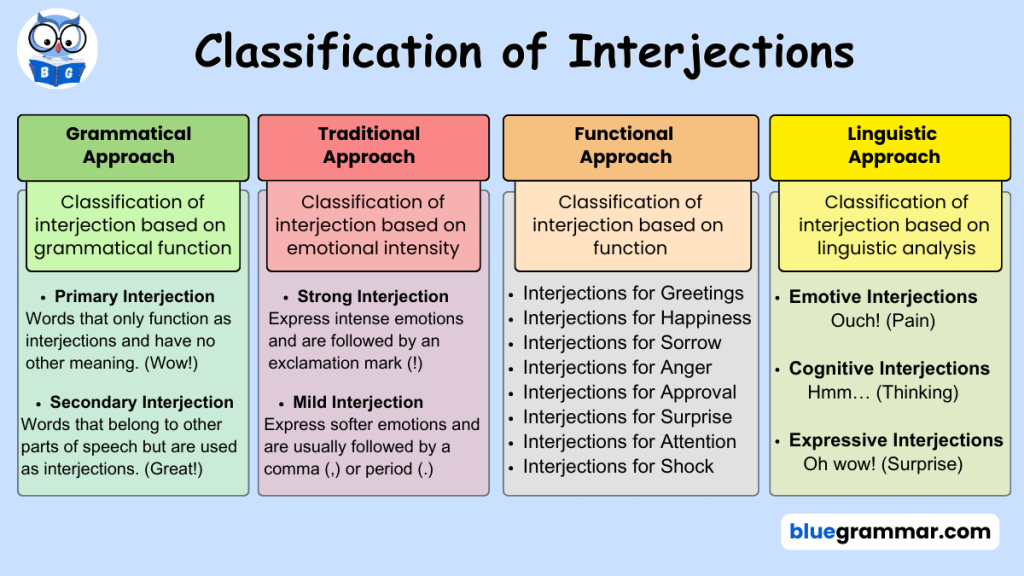
Interjections are words or phrases used to express sudden emotions or feelings. They are not grammatically related to other parts of a sentence but serve to convey emotions like joy, surprise, pain, anger, or approval. Interjections can be classified using different approaches: grammatical, traditional, functional, and linguistic. The words that are commonly used as Interjections are as follows:
Hurrah! , Alas! , Oh no! , Oh my God! , What! , etc.
Grammatical Approach for Types of Interjections
This classification is based on the grammatical function of interjections.
1. Primary Interjections
Primary interjections are words that only function as interjections and have no other meaning in the language. These words are often used independently to express emotions. Examples include:
- Wow! Ouch! Yay! Oh!
2. Secondary Interjections
Secondary interjections are words that belong to other parts of speech but are used as interjections to express emotions. Examples include:
- Great! Well! Indeed! Oh dear!
Traditional Approach for Types of Interjections
The traditional approach classifies interjections based on their emotional intensity.
1. Strong Interjections
Strong interjections express intense emotions and are usually followed by an exclamation mark (!). These interjections convey strong feelings such as surprise, anger, or excitement. Examples include:
- Wow! Ouch! Hooray! Alas!
2. Mild Interjections
Mild interjections express softer emotions and are usually followed by a comma (,) or period (.). They are less intense than strong interjections. Examples include:
- Well, Oh, Hmm. Ah.
Functional Approach for Classification of Interjections
This approach categorizes interjections based on their function in communication.
Interjections for Greetings
Such interjections are used in sentences to show the emotions of warmness to the person meeting with.
Examples:
- Good morning! It’s great to see you.
- Hey! When you came here?
- Hello! I am Sadaf.
Interjections for Happiness
Such interjections are used in sentences to show happiness or joy on any happy occasion.
Examples:
- Yay! We won!
- Hurrah! I’ve won!
- Wow! What a pleasant weather!
Interjections for Sorrow
Such interjections are used in sentences to express the emotion of sadness about something unfortunate has happened.
Examples:
- Alas! He could not recover from his illness.
- Ouch! That hurts.
- Oops, I’m sorry. It was hot.
- Alas! His friend died.
Interjections for Anger
Such interjections are used in sentences to express the anger about something unfortunate has happened by someone’s mistake or carelessness.
Examples:
- Excuse me! I am not a beggar.
Interjections for Approval
Such interjections are used in sentences to show the sense of agreement or approval for something.
Examples:
- Well done! You got first position.
- Brilliant! You arrived here in time.
Interjections for Surprise
Such interjections are used in sentences to express the shock about something happened.
Examples:
- What! What have you done?
Interjections for Attention
Such interjections are used in sentences to draw the attention of someone.
Examples:
- Hey! Let’s go on a picnic!
- Yo! What is going on?
- Look! Jam is so happy.
- Listen! I am starving.
Interjections for Shock
Used to express extreme shock or disbelief.
- What!
- Oh my God!
- Whoa!
Linguistic Approach for Types of Interjections
This approach classifies interjections based on linguistic analysis.
Emotive Interjections
Emotive interjections are used to express spontaneous emotions such as pain, joy, sadness, excitement, or fear. These interjections often stand alone in a sentence and are used to convey strong feelings without the need for additional context. They are commonly used in both spoken and written language to make communication more expressive.
Examples:
- Ouch! (Pain)
- Wow! (Surprise)
- Hooray! (Excitement)
- Alas! (Sorrow)
- Oh no! (Disappointment)
Cognitive Interjections
Cognitive interjections are used to indicate hesitation, contemplation, or thought processes. These interjections help to signal that the speaker is pausing to think, expressing uncertainty, or trying to gather their thoughts. They are commonly used in both casual and formal conversations to reflect internal reasoning or hesitation.
Examples:
- Hmm… (Thinking or considering something)
- Uh… (Uncertainty or searching for words)
- Er… (Doubt or hesitation before speaking)
Expressive Interjections
Expressive interjections emphasize emotions in a more exaggerated or dramatic way. They add a deeper level of emotion to a statement and often highlight a speaker’s reaction. These interjections can be used to show excitement, relief, concern, or admiration in a conversation.
Examples:
- Oh wow! (Surprise or admiration)
- Ahh! (Relief or relaxation)
- Oh dear! (Concern or worry)
Interjections play a crucial role in communication by helping convey emotions in a direct and impactful manner. Whether used in formal or informal speech, they enhance the expressiveness of language.