Definition of an Adjective
An adjective is defined as a word that provides information about a noun, pronoun, or noun phrase. It adds additional details about a noun or pronoun by indicating its quality, kind, or degree. Look at the examples below:
Sana gave me eight apples.
The mouse is little.
The sky is blue and clear today.
She wore a beautiful red dress to the party.
In the first example, the word “eight” tells us the quantity of apples, making it an adjective. In the second example, the word “little” describes the quality of the mouse. Similarly, “blue” and “beautiful” in the other examples describe the appearance of the sky and the dress, respectively.
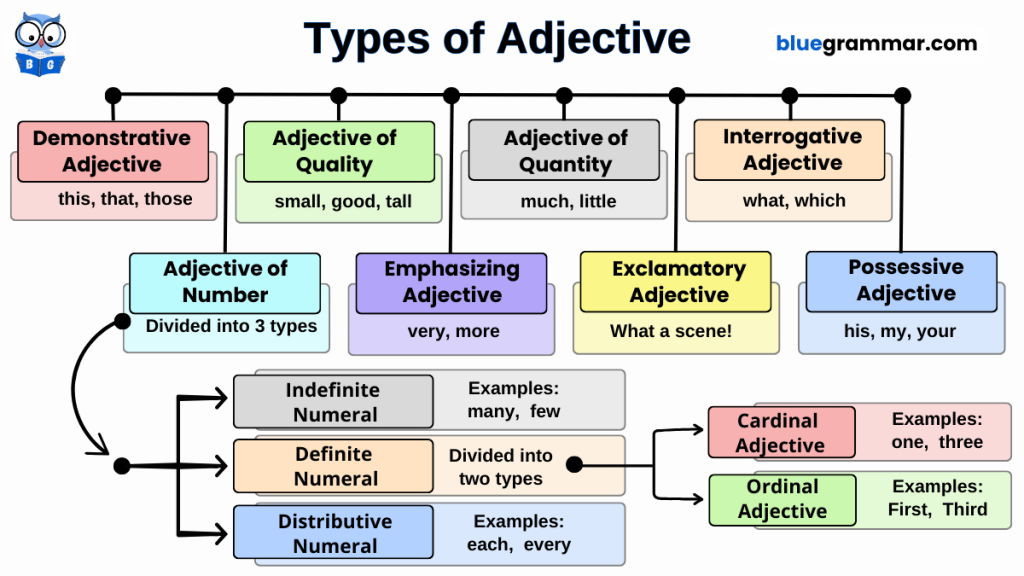
Types of Adjectives
Adjectives are categorized into several types, including:
Adjectives of Quality
Adjectives of Quantity
Numeral Adjectives
Demonstrative Adjectives
Possessive Adjectives
Interrogative Adjectives
Emphasizing Adjectives
Exclamatory Adjectives
Adjectives of Quality
Adjectives of quality describe the kind, quality, or degree of a noun or pronoun. They are also called descriptive adjectives.
Examples:
He ate a big mango.
Hassan is an honest man.
The child is foolish.
The Arabic language is not hard to learn.
The mountains in Switzerland are stunning.
Some adjectives of quality originate from proper nouns, such as “Arabic” in the fourth example. These are called proper adjectives and generally fall under the category of adjectives of quality.
Adjectives of Quantity
These adjectives indicate the quantity of a noun and answer the question: How much?
Common Adjectives of Quantity: some, much, no, any, little, enough, great, half, sufficient.
Examples:
Take great care of your grandma’s health.
The pay is enough for my expenses.
Half of the papers were checked.
He has little patience.
There isn’t much water left in the bottle.
Adjectives of Number (Numeral Adjectives)
These adjectives tell us how many things or people are involved or indicate their order in a series. Numeral adjectives are classified into three types:
1. Definite Numeral Adjectives: Indicate an exact number.
Cardinals: one, two, three, etc.
Example: I have three pairs of scissors.
-Ordinals: first, second, third, etc.
Example: She was the first one to arrive at the airport.
2. Indefinite Numeral Adjectives: Do not specify an exact number.
Common words: no, all, few, many, some, several, any, etc.
Examples:
All the cats are sleeping.
I have taken several different baking lessons.
There are no pedestrians on the street.
3. Distributive Numeral Adjectives: Refer to each item of a group.
Common words: each, every, either, neither.
Examples:
Each student must take their turn.
Neither proposal is acceptable.
Every child deserves a good education.
Demonstrative Adjectives
Demonstrative adjectives point to a specific person or thing and answer the question: Which one?
Common Demonstrative Adjectives: this, that, these, those, such.
Examples:
This is my assignment.
Those are spicy dishes.
Such an attitude will cause him failure.
That book belongs to me.
Interrogative Adjectives
These adjectives are used in questions. When what, whose, and which are used with a noun to form a question, they become interrogative adjectives.
Examples:
Which way leads to the mall?
What time is it?
Whose duty is it today?
Possessive Adjectives
Possessive adjectives show ownership.
Common Possessive Adjectives: my, your, our, its, his, her, their.
Examples:
My daily routine is pretty simple.
Your shoelaces are loose.
The cat is licking its paws.
They are doing their work.
Emphasizing Adjectives
These adjectives add emphasis to a sentence.
Examples:
This is the very book I want.
Sarah saw the robbery with her own eyes.
I met the man himself.
Exclamatory Adjective
An exclamatory adjective is used to express strong emotions like excitement or fear. The most common one is “what.”
Examples:
What nonsense!
What a spectacular view!
What foolishness!
Degrees of Comparison
Adjectives can change in form to indicate a comparison. These changes determine the degree of comparison, which can be:
1. Positive Degree: The adjective is in its simplest form.
2. Comparative Degree: The adjective compares two things.
3. Superlative Degree: The adjective compares more than two things.
Positive Degree
An adjective with a positive degree is an adjective in its simple and original form. There is no comparison going on with anything. It just lets it known that some quality exists in something or someone. Look at the following examples.
Examples:
The bus I took yesterday was very fast.
My dog is very intelligent.
This is a good calculator.
Comparative Degree
The comparative degree of an adjective show that the presence of a quality in one thing is more or higher than its presence in the Positive. This degree is used when the comparison of two things is happening. Let’s see the examples below.
Examples:
The bus I took yesterday was faster than the one I took today.
My dog is more intelligent than my friend’s dog.
This calculator is better than the old one.
Superlative Degree
The Superlative Degree of Comparison is used when the some quality in one thing or person is highest than anything or anyone else. Superlative degree is used when a thing or person is in comparison against more than one thing or person.
Examples:
The bus I took yesterday was the fastest.
My dog is the most intelligent dog.
This is the best calculator I have ever used.