The Nine Parts of Speech in English Grammar
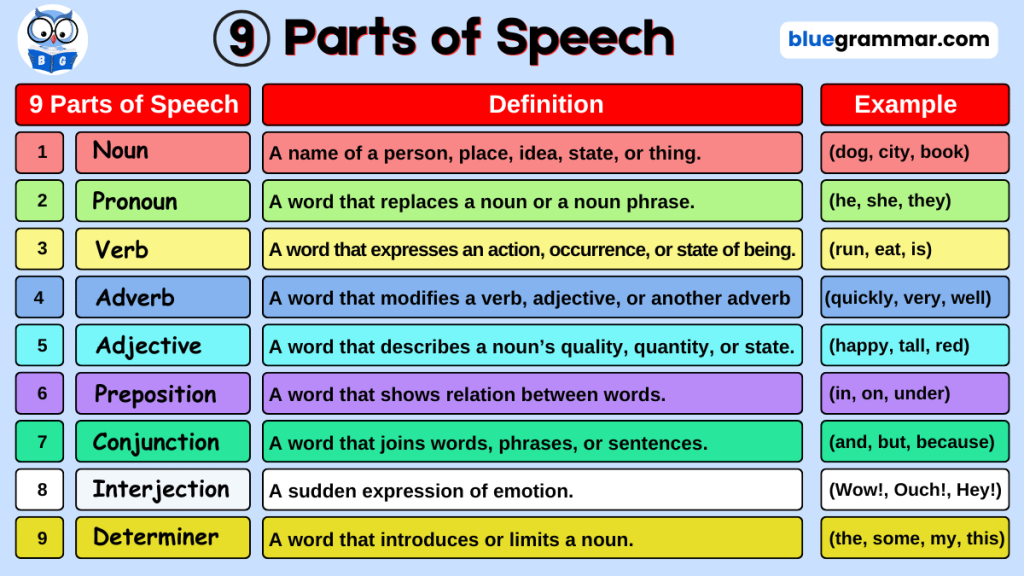
In English grammar, there are nine parts of speech. They are: noun, pronoun, verb, adverb, adjective, preposition, conjunction, interjection, and determiner. These parts of speech are the building blocks of the English language. Each part of speech has a special job in a sentence.
The Shift in Grammar: Eight vs. Nine Parts of Speech
In English grammar, there is some debate about how many parts of speech there are—eight or nine. Traditionally, many grammar resources list eight parts of speech, which include noun, pronoun, verb, adverb, adjective, preposition, conjunction, and interjection. However, modern linguistic studies recognize nine parts of speech by treating determiners as a separate category. Determiners include words like the, a, some, and this, and they are used to introduce and specify nouns. In older grammar approaches, determiners were often grouped with adjectives since both words provide more information about nouns. However, in modern grammar, determiners are considered distinct because they serve a different function—they determine or clarify the noun rather than describe its qualities.
Another point of confusion arises in some places where articles (such as the and a) are seen as separate parts of speech. This categorization sometimes leads to debates about whether determiners and articles should be treated as one category or two. The distinction between different grammar systems shows how language evolves, and the classification of parts of speech depends on the approach a person follows.
The Importance of Learning Parts of Speech
Learning the parts of speech is important because they help us understand how words work together in a sentence. By knowing the function of each part of speech, we can use words correctly and make our communication clearer. Each part of speech helps to form the structure of a sentence. Without these parts of speech, sentences would not make sense. For example, a sentence like “She quickly runs” is easy to understand because the words follow the rules of grammar.
The Nine Parts of Speech
Here’s a simple explanation of each part of speech with examples:
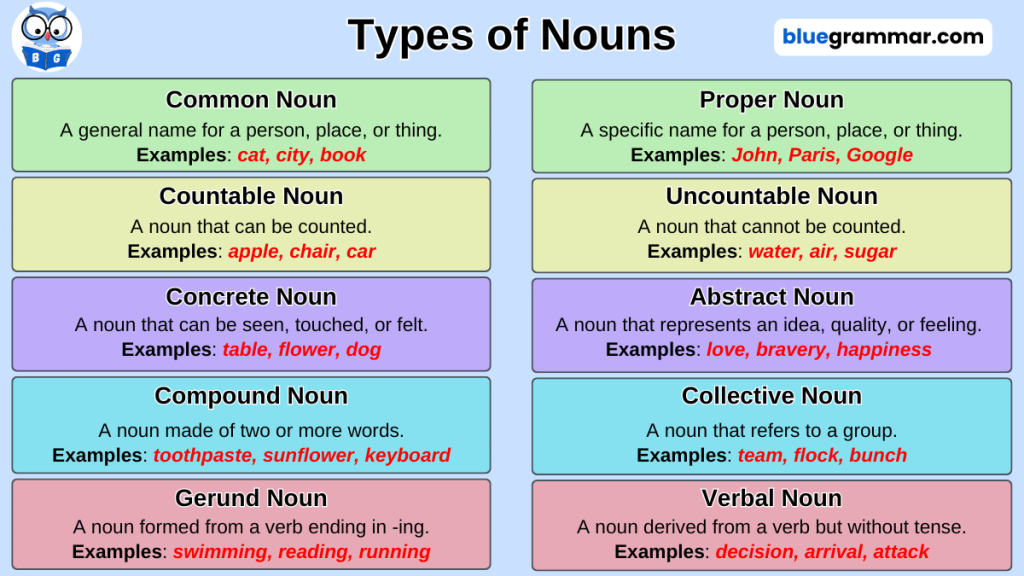
1. Noun
A noun is a word that names a person, place, thing, or idea. It can act as a subject, object, or complement in a sentence.
Example:
- Sara reads books. (Sara is a noun as the subject, books is a noun as the object.)
- The cat sleeps. (Cat is a noun as the subject.)
- Honesty is important. (Honesty is a noun as the subject.).
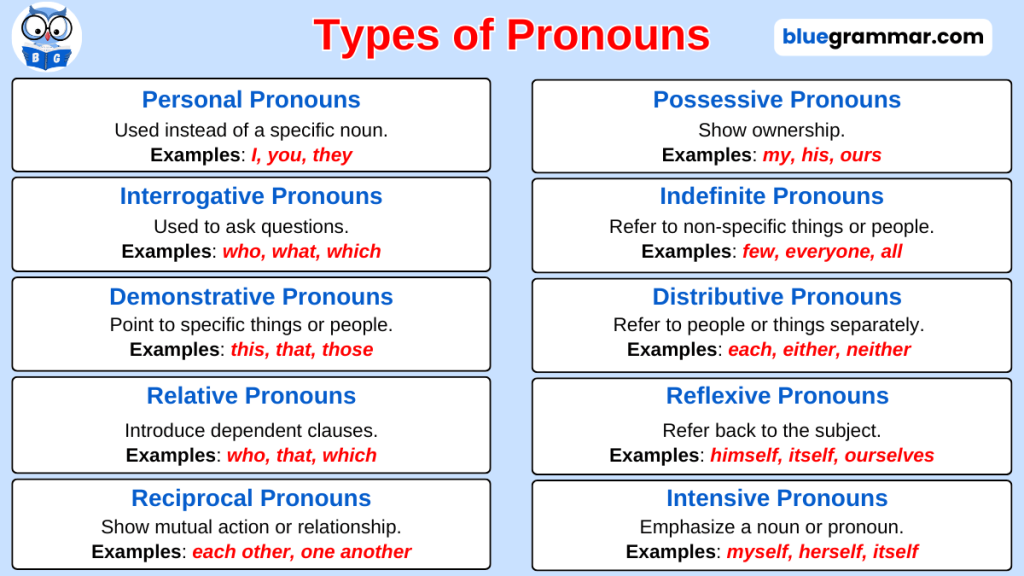
2. Pronoun
A pronoun is defined as a word that is used in place of a noun to avoid repetition and make sentences clearer and more natural. Pronouns help us speak and write more efficiently by replacing names or noun phrases that are already known from the context.
Let’s understand this with a short paragraph:
“Sara is a brilliant student. Sara goes to school every day. Sara completes all her homework on time. Sara’s teachers appreciate Sara.”
In the above paragraph, the name “Sara” is repeated many times, which makes the writing sound repetitive and unnatural. We can make the paragraph smoother and more concise by using pronouns:
“Sara is a brilliant student. She goes to school every day and completes all her homework on time. Her teachers appreciate her.”
Here, “she” and “her” are pronouns that take the place of the noun “Sara.”
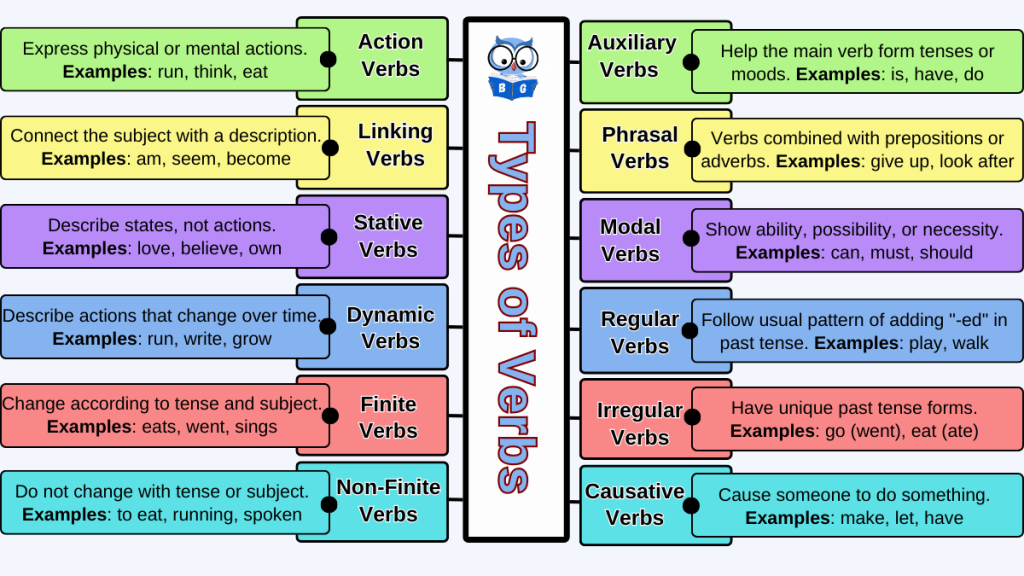
3. Verb
A verb is a word that shows an action, an event, or a state of being. It is the heart of a sentence, telling us what the subject is doing or what is happening.
Verbs can:
- Show action: The cat sleeps all day.
- Show something done to someone: A stranger patted the stray cat.
- Show a state: The cat is alive, fortunately.
Without a verb, a sentence usually doesn’t make sense. While short replies like “Yes” or “Indeed” may work in casual speech, proper sentences require verbs.
4. Adverb
An adverb is a word that modifies a verb, an adjective, or another adverb. It tells us how, when, or where something happens.
For example:
- Ali walks swiftly. (Modifies the verb “walks” – how he walks)
- She took the grocery out very carefully. (Modifies the adverb “carefully” – to what extent)
- That is a really sweet child. (Modifies the adjective “sweet” – to what degree)
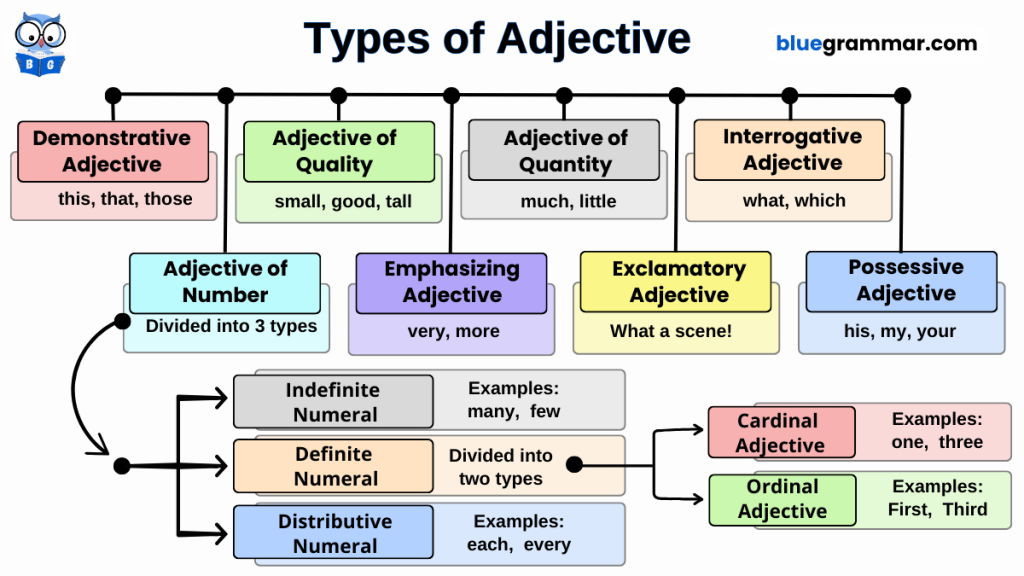
5. Adjective
An adjective is a word that gives more information about a noun, pronoun, or noun phrase. It describes things like quantity, quality, kind, or degree.
For example:
- Sana gave me eight apples. (Describes the quantity of apples)
- The mouse is little. (Describes the size of the mouse)
- The sky is blue and clear today. (Describes the appearance of the sky)
- She wore a beautiful red dress to the party. (Describes the appearance of the dress).
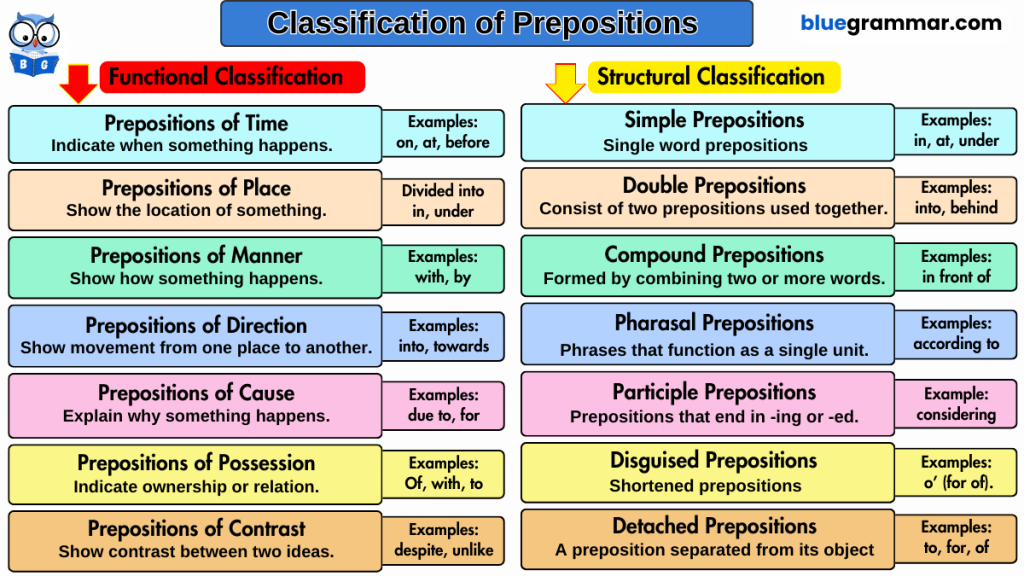
6. Preposition
Prepositions are words that come before nouns or pronouns. They show how a person or thing is related to something else.
For example:
- The child jumped off the bed. (shows the relationship between the jump and the bed)
- There is a bee in the jar. (shows the relationship between the bee and the jar)
- Hani is fond of cheesecakes. (shows the relationship between being fond and cheesecakes)
- In these examples, off, in, and of are prepositions.
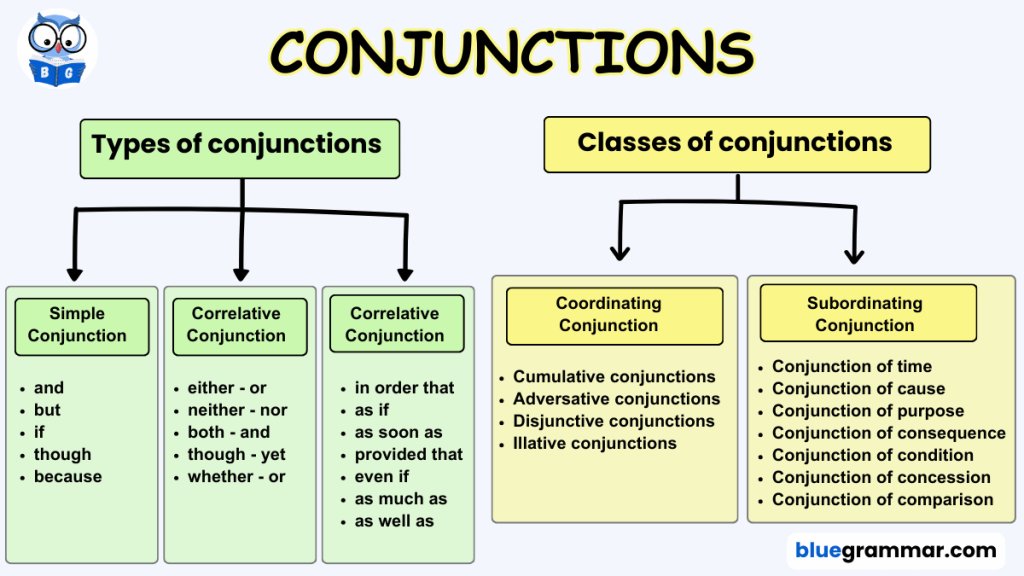
7. Conjunction
A conjunction is a word that joins sentences, clauses, or sometimes words together. It helps make sentences shorter and more connected. Unlike relative adverbs and pronouns, conjunctions only serve to join, with no other role.
For example:
- The teacher is young, but she is talented. (joins two sentences)
- Sara and Hania are sisters. (joins two words)
- In the first example, but connects two sentences, making the sentence more compact. In the second example, and simply joins two words.
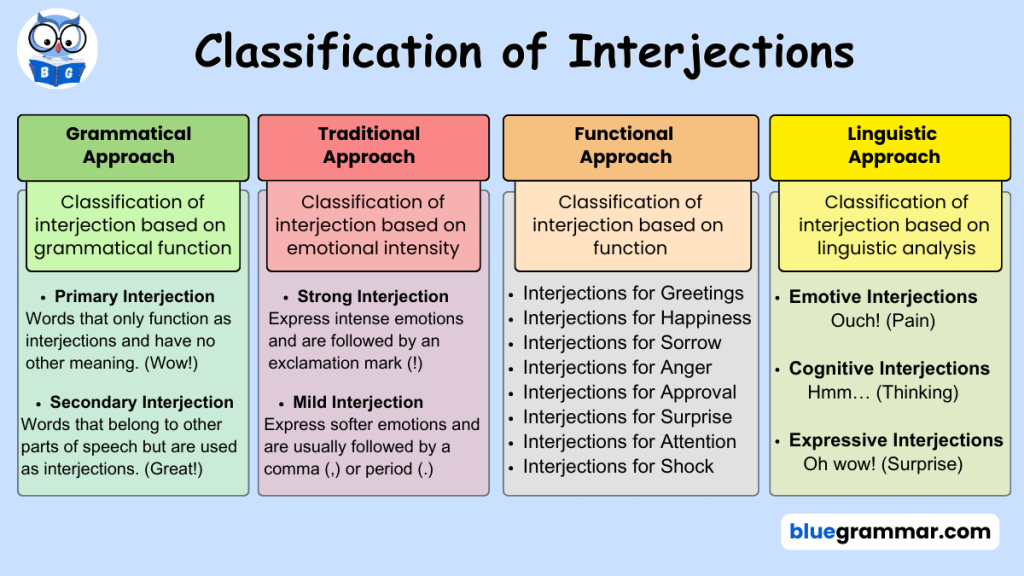
8. Interjection
Interjections are words or phrases used to express sudden emotions or feelings. They are not grammatically related to other parts of a sentence but serve to convey emotions like joy, surprise, pain, anger, or approval. Interjections can be classified using different approaches: grammatical, traditional, functional, and linguistic. The words that are commonly used as Interjections are as follows:
Hurrah! , Alas! , Oh no! , Oh my God! , What! , etc.
9. Determiner
A determiner is a word that introduces a noun and gives more information about it. It can tell us about quantity, possession, or definiteness.
Examples: the, a, this, my, some.
Why Learning the Parts of Speech is Necessary
When we understand the parts of speech, we can use words more effectively. Knowing where to place nouns, verbs, adjectives, and other parts of speech in a sentence helps us communicate clearly. For example, you would not say “She the book reads” because the sentence does not follow grammar rules. Instead, you say “She reads the book,” which is correct.
In conclusion, the nine parts of speech form the foundation of English grammar. By learning how each one works, we can improve our writing and speaking skills, making our sentences easier to understand and more effective in communication.