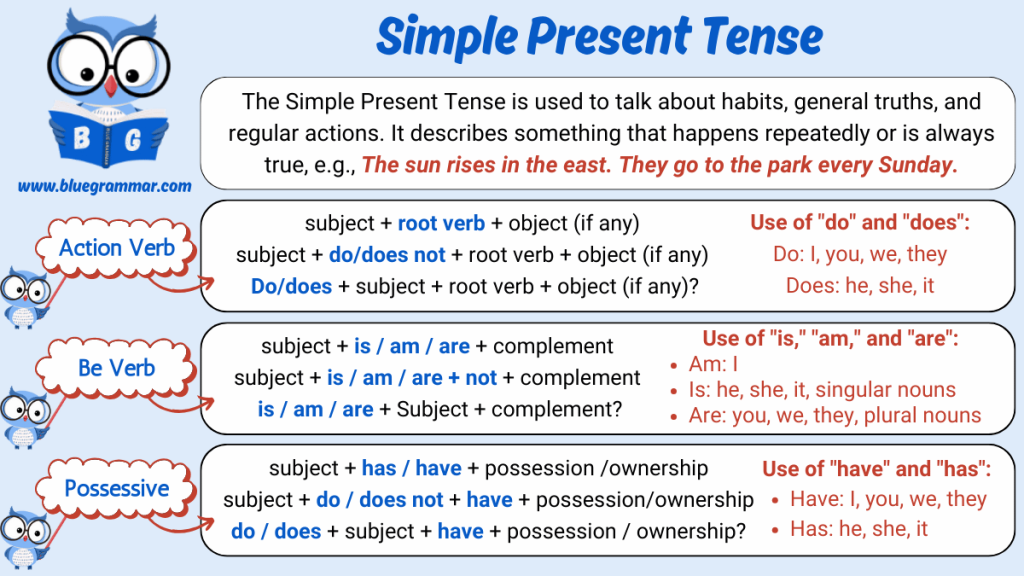
Present Simple Tense : Action Verb
The Present Simple Tense is used with action verbs to describe habits, regular actions, general truths, and repeated activities. Action verbs refer to physical or mental activities like “run,” “write,” “read,” or “think.”

Making Positive Sentences
Structure:
Subject + root verb (+ s/es for he, she, it) + object (if any)
Examples with Object:
He reads books every evening.
They play cricket every weekend.
Examples without Object:
She runs every morning.
I sleep early.
Making Negative Sentences
Structure:
Subject + do/does not + root verb + object (if any)
“Do” is used with I, you, we, they
“Does” is used with he, she, it
Examples with Object:
He does not eat meat.
We do not watch movies on weekdays.
Examples without Object:
She does not run in the morning.
I do not sing often.
Making Interrogative Sentences
Structure:
Do/does + subject + root verb + object (if any)?
Examples with Object:
Does he read novels regularly?
Do they like ice cream?
Examples without Object:
Does she cook every day?
Do you exercise?
Present Simple Tense : Be Verb
“Be” verbs in the present simple are is, am, and are, used to describe states, characteristics, identity, or situations rather than actions.

Making Positive Sentences
Structure:
Subject + is/am/are + complement
Examples with Complement (object-like phrase):
She is a teacher.
We are friends.
Examples without Complement (adjective or preposition phrase):
I am happy.
They are at home.
Making Negative Sentences
Structure:
Subject + is/am/are + not + complement
Examples with Complement:
He is not a doctor.
We are not busy today.
Examples without Complement:
I am not tired.
You are not in the room.
Making Interrogative Sentences
Structure:
Is/am/are + subject + complement?
Examples with Complement:
Is she your sister?
Are they your neighbors?
Examples without Complement:
Am I late?
Is he here?
Present Simple Tense : Possessive Verb
Possessive verbs in the present simple are have and has, which show possession or ownership.

Making Positive Sentences
Structure:
Subject + has/have + object/possession
Examples with Object:
She has a car.
I have a laptop.
Examples without Object (general possession):
We have time.
He has money.
Making Negative Sentence:
Structure:
Subject + do/does not + have + object
Examples with Object:
He does not have a pen.
They do not have a plan.
Examples without Object:
I do not have time.
She does not have experience.
Making Interrogative Sentences
Structure:
Do/does + subject + have + possession?
Examples with Object:
Does he have a bicycle?
Do you have a ticket?
Examples without Object:
Do we have time?
Does she have support?